Hadoop for Big data
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open source, Java-based programming framework that supports the processing and storage of extremely large datasets in a distributed computing environment. It is part of the Apache project sponsored by the Apache Software Foundation.

- Ability to store and process huge amounts of any kind of data, quickly.
- Computing power.
- Fault tolerance.
- Flexibility
- Low cost.
- Scalability.
What is MapReduce
MapReduce – a parallel processing software framework. It is comprised of two steps. Map step is a master node that takes inputs and partitions them into smaller subproblems and then distributes them to worker nodes. After the map step has taken place, the master node takes the answers to all of the subproblems and combines them to produce output
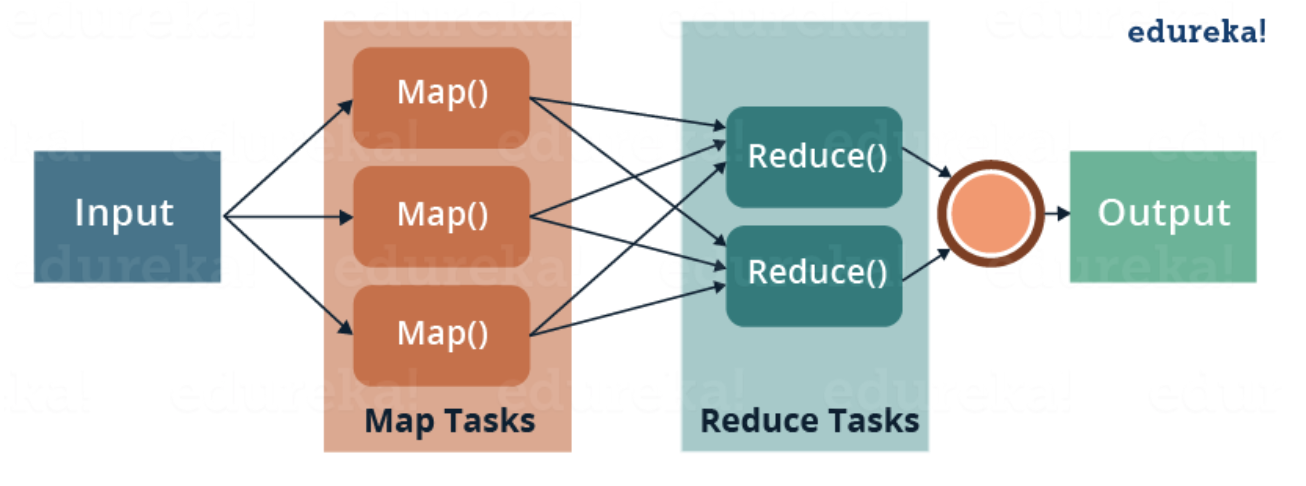
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware. HDFS is highly fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware. HDFS provides high throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications that have large data sets. It relaxes a few POSIX requirements to enable streaming access to file system data.

Set up with Hadoop
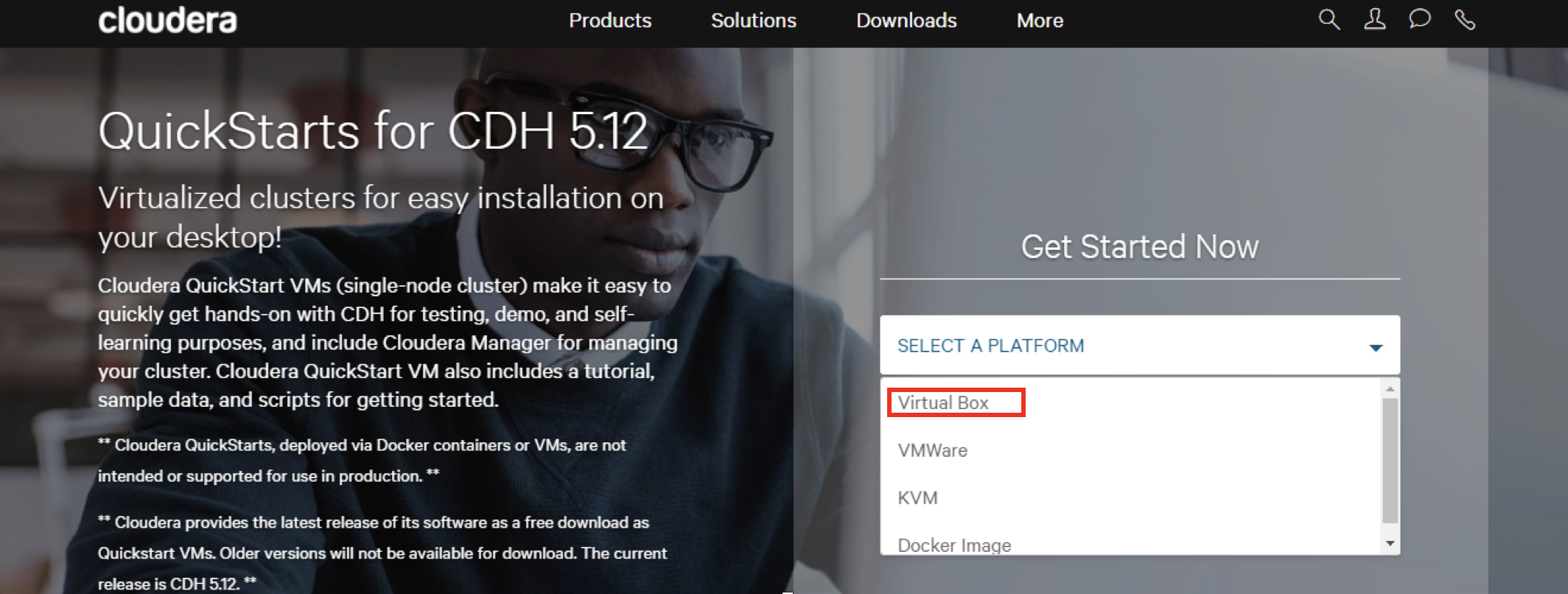
1.Download the platform Virtual Box from Cloudera VMs:
link:Cloudera downloads
2.Select “Virtual Box” and then click on “get it now”. And it will ask you to fill out some information about you or sign in. After that, agree with the contract. And it will start downloading the Virtual Box.
3.Unzip the file, you will see two file under the folder

4.Download the VirtualBox
VirtualBox select OS X hosts for mac user.
This is the VirtualBox interface looklike:
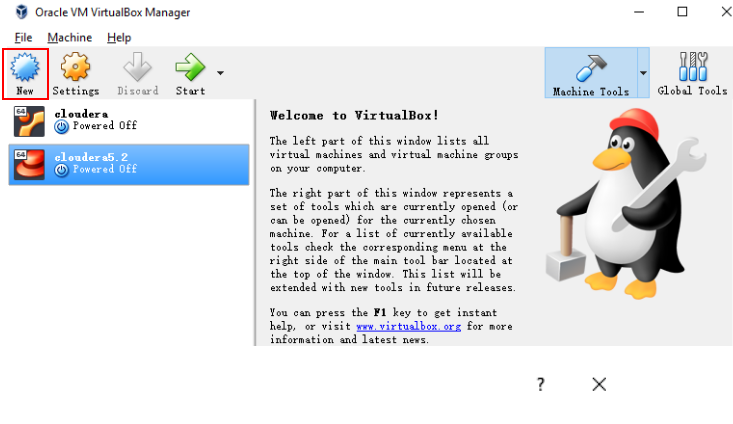
5.Then slecte “File” –> “import Application” to import “cloudera-quickstart-vm-5.12.0-0-virtualbox.ovf”


How to Install RStudio Server on CentOS
(RStudio Server is the web edition of RStudio which is a series of tools designed to facilitate the coding job using the R programming language.)
Step 1: Update the system
Log in as a sudo user, and then execute the below commands:
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum update
sudo shutdown -r now
Step 2: Install R
sudo yum install R -y
Step 3: Install RStudio Server
Install the latest stable release of RStudio Server.
cd
wget https://download2.rstudio.org/rstudio-server-rhel-1.0.136-x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install --nogpgcheck rstudio-server-rhel-1.0.136-x86_64.rpm -y
Note: find the latest release of RStudio Server from this webset: official download page
Step 4: Access RStudio Server from a web browser
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8787/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Project abstract
Data source: Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) Data Set This data source is use to predict whether the cancer is benign or malignant
Build Prediction Model in R
Load Data:
require(caret)
require(mlbench)
# load the data
cancerData <- read.csv("data.csv", sep = ",", header = T)
Feature selection:
set.seed(123)
# calculate correlation matrix
correlationMatrix <- cor(cancerData[,3:32])
# find attributes that are highly corrected (ideally >0.75)
highlyCorrelated <- findCorrelation(correlationMatrix, cutoff=0.5)
# print indexes of highly correlated attributes
print(highlyCorrelated)
# define the control using a random forest selection function
control <- rfeControl(functions=rfFuncs, method="cv", number=10)
# run the RFE algorithm
results <- rfe(cancerData[,3:32], cancerData[,2], sizes=c(3:32), rfeControl=control)
# summarize the results
print(results)
The list of chosen features and Plot of features by accuracy
predictors(results)
plot(results, type=c("g", "o"))
Subsetting the data using the selected features
features <- predictors(results)
newdata <- cancerData[, features]
newdata$diagnosis <- cancerData$diagnosis
Partition the data into training and testing being 70% and 30% resoectively.
inTrain <- createDataPartition(y = newdata$diagnosis ,
p=0.7, list=FALSE)
training <- newdata[inTrain,]
testing <- newdata[-inTrain,]
dim(training)
Generalized Linear Model
set.seed(323)
modelFit1 <- train(diagnosis ~.,data=training, preProcess = c("center", "scale"), method="glm")
pred1 <- predict(modelFit1,newdata=testing)
confusionMatrix(pred1,testing$diagnosis)
MapReduce Simulation
Run MapReduce Locally.
$ bin/hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.9.0.jar grep input output 'dfs[a-z.]+'
Web Application
Support or Contact
Having trouble with Pages? Check out our documentation or contact support and we’ll help you sort it out.